Cleaning Up GRACC
The GRid ACcounting Collector (GRACC) is the OSG’s new version of accounting software, replacing Gratia. It has been running in production since March 2017. Last week, on Friday November 3rd, we held a GRACC Focus Day. Our goal was to clean up data that is presented in GRACC. My changes where:
- Update the GRACC-Collector to version 1.1.8. The primary change in this release is setting the messages sent to RabbitMQ to be “persistent”. The persistent messages are then saved to disk in order to survive a RabbitMQ reboot.
- Use case-insenstive comparisons to determine the Open Science Grid Information Management system (OIM) information. This was an issue with GPGrid (Fermilab), which was registered as GPGRID.
- Set the
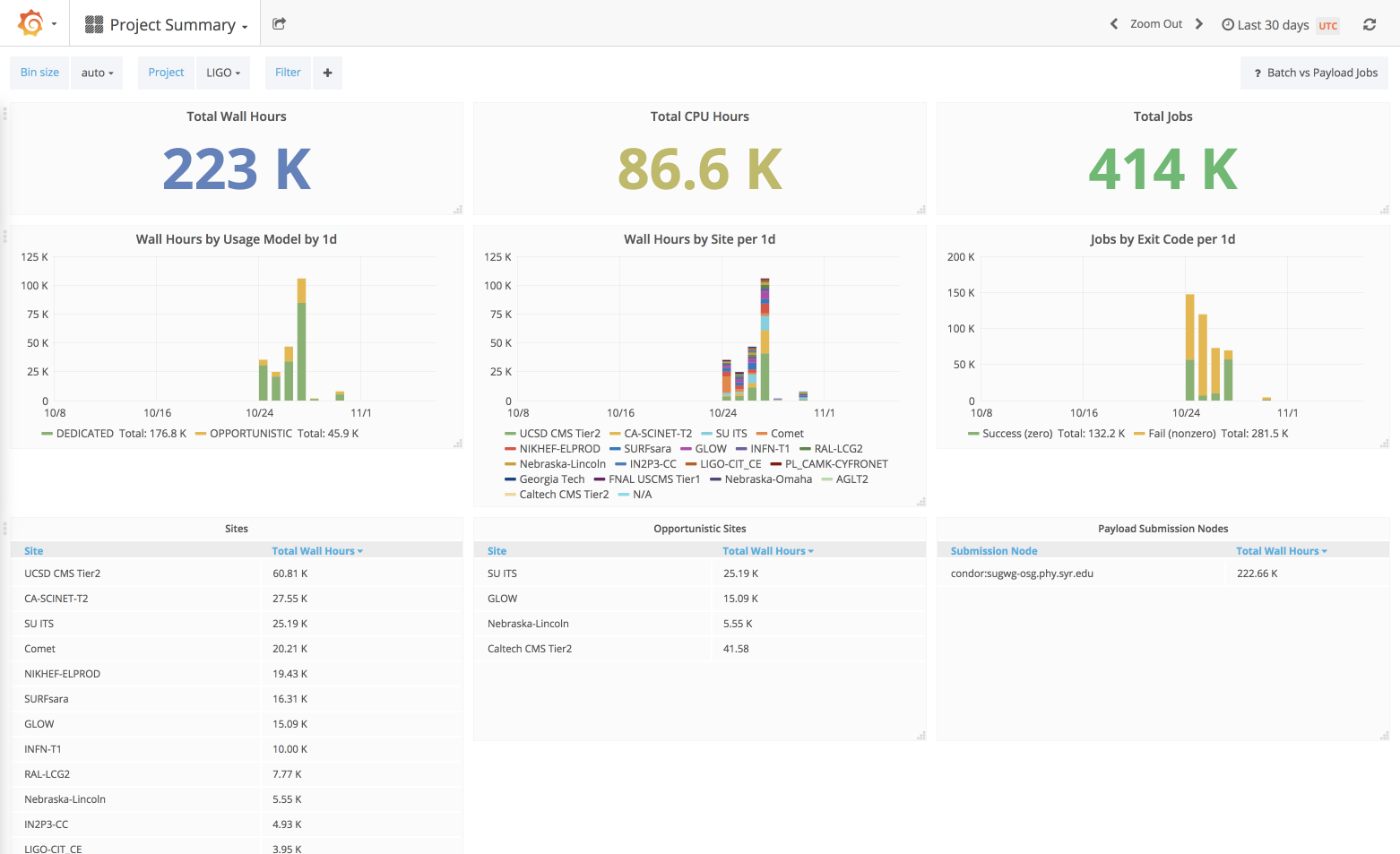
OIM_Siteequal to theHost_descriptionattribute if the OIM logic is unable to determine the registered OIM site. This is especially useful for the LIGO collaboration, which uses sites in Europe that are not registered in OIM. Now, instead of a lot of Unknown sites listed on the LIGO site listing, it shows the somewhat reported site name of where the job ran.
Regular Expression Corrections
One of the common problems we have in GRACC is poor data coming from the various probes installed at hundreds of sites. We don’t control the data coming into GRACC, so occasionally we must make corrections to the data for clarity or correctness. One of these corrections is misreporting the “site” that the jobs ran on.
In many instances, the probe is unable to determine the site and simply lists the hostname of the worker node where the job ran. This can cause the cardinality of sites listed in GRACC to increase dramatically as we get new hostnames inserted into the sites listing. If the hostnames are predictable, a regular expression matching algorithm can match a worker node hostname to a proper site name.
The largest change for GRACC was the regular expression corrections. With this new feature, GRACC administrators can set corrections to match on attributes using regular expression patterns. For example, consider the following correction configuration.
[[Corrections]]
index = 'gracc.corrections'
doc_type = 'host_description_regex'
match_fields = ['Host_description']
source_field = 'Corrected_OIM_Site'
dest_field = 'OIM_Site'
regex = true
This configuration means:
Match the
Host_descriptionfield in the incoming job record with the regular expressionHost_descriptionfield in the corrections table. If they are a match, take the value in theCorrected_OIM_Sitefield in the corrections table and place it into theOIM_Sitefield in the job record.
And the correction document would look like:
{
"_index": "gracc.corrections-0",
"_type": "host_description_regex",
"_id": "asldkfj;alksjdf",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"Host_description": ".*\.bridges\.psc\.edu",
"Corrected_OIM_Site": "PSC Bridges",
}
}
The regular expression is in the Host_description FIELD.
So, if the incoming job record is similar to :
{
...
"Host_description": "l006.pvt.bridges.psc.edu"
...
}
Then the correction would modify or create values such that the final record would approximate:
{
...
"Host_description": "l006.pvt.bridges.psc.edu",
"OIM_Site": "PSC Bridges",
"RawOIM_Site": ""
...
}
Note that the Host_description field stays the same. We must keep it the same because it is used in record duplicate detection. If we modified the field and resummarized previous records, then it would cause multiple records to represent the same job.
